Enable CORS Support in Cosmos DB using PowerShell
Support for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) was recently added to Cosmos DB. If you want to enable CORS on an existing Cosmos DB account or create a new Cosmos DB account with CORS enabled it is very easy to do with Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates or the Azure Portal.
But what if you’re wanting to find out the state of the CORS setting on an account or set it using PowerShell? Well, look no further.
The Cosmos DB PowerShell module (version 3.0.0 and above) supports creating Cosmos DB accounts with CORS enabled as well as updating and removing the CORS headers setting on an existing account. You can also retrieve the CORS setting for an existing Cosmos DB account.
The first thing you need to do is install the CosmosDB PowerShell module from the PowerShell Gallery by running this in a PowerShell console:
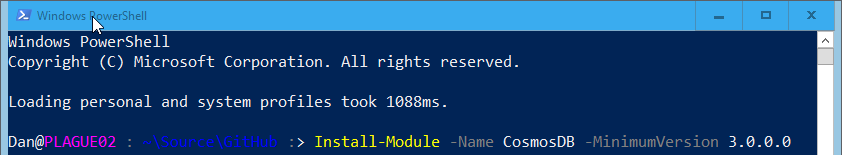
This will also install the Az PowerShell modules Az.Accounts and Az.Resources modules if they are not installed on your machine. The *-CosmosDbAccount functions in the CosmosDB module are dependent on these modules.
Note: The CosmosDB PowerShell module and the Az PowerShell modules are completely cross-platform and support Linux, MacOS and Windows. Running in either Windows PowerShell (Windows) or PowerShell Core (cross-platform) is supported.
Versions of the CosmosDB PowerShell module earlier than 3.0.0.0 use the older AzureRm/AzureRm.NetCore modules and do not support the CORS setting.
Before using the CosmosDB PowerShell module accounts functions to work with CORS settings you’ll first need to authenticate to Azure using the Az PowerShell Modules. If you’re planning on automating this process you’ll want to authenticate to Azure using a Service Principal identity.
Side note: if you’re using this module in an Azure DevOps build/release pipeline the Azure PowerShell task will take care of the Service Principal authentication process for you:
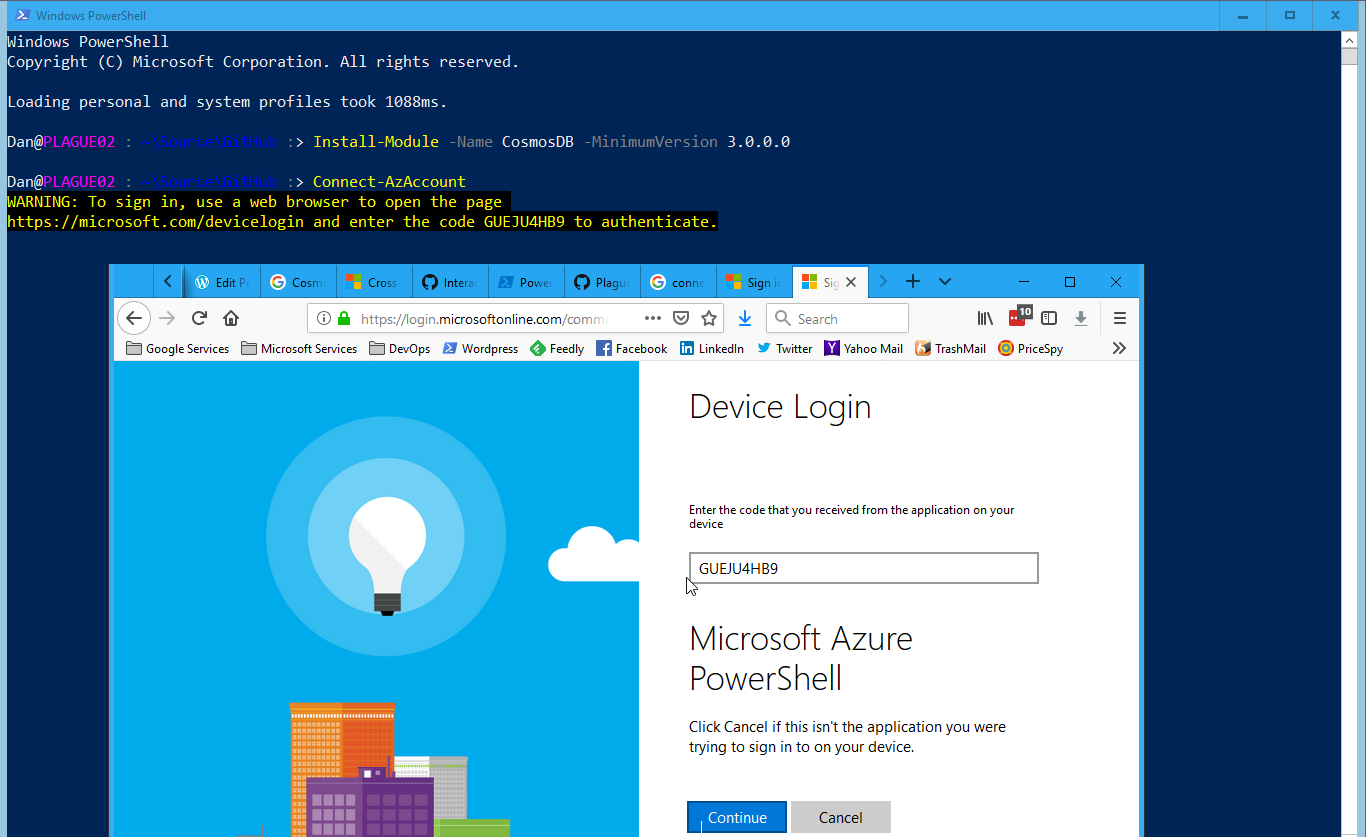
But if you’re just doing a little bit of experimentation then you can just use an interactive authentication process.
To use the interactive authentication process just enter into your PowerShell console:
then follow the instructions.
Once you have authenticated to Azure, you can use the New-CosmosDbAccount function to create a new account:
 This will create a new Cosmos DB account with the name dsrcosmosdbtest in the resource group dsrcosmosdbtest-rgp in the West US location and with CORS allowed origins of https://www.fabrikam.com and https://www.contoso.com.
This will create a new Cosmos DB account with the name dsrcosmosdbtest in the resource group dsrcosmosdbtest-rgp in the West US location and with CORS allowed origins of https://www.fabrikam.com and https://www.contoso.com.
Important: the New-CosmosDbAccount command assumes the resource group that is specified in the ResourceGroup parameter already exists and you have contributor access to it. If the resource group doesn’t exist then you can create it using the New-AzResourceGroup function or some other method.
It will take Azure a few minutes to create the new Cosmos DB account for you.
Side note: But if you want your PowerShell automation or script to be able to get on and do other tasks in the meantime, then add the -AsJob parameter to the New-CosmosDbAccountcall. This will cause the function to immediately return and provide you a Job object that you can use to periodically query the state of the Job. More information on using PowerShell Jobs can be found here.
Be aware, you won’t be able to use the Cosmos DB account until the Job is completed.
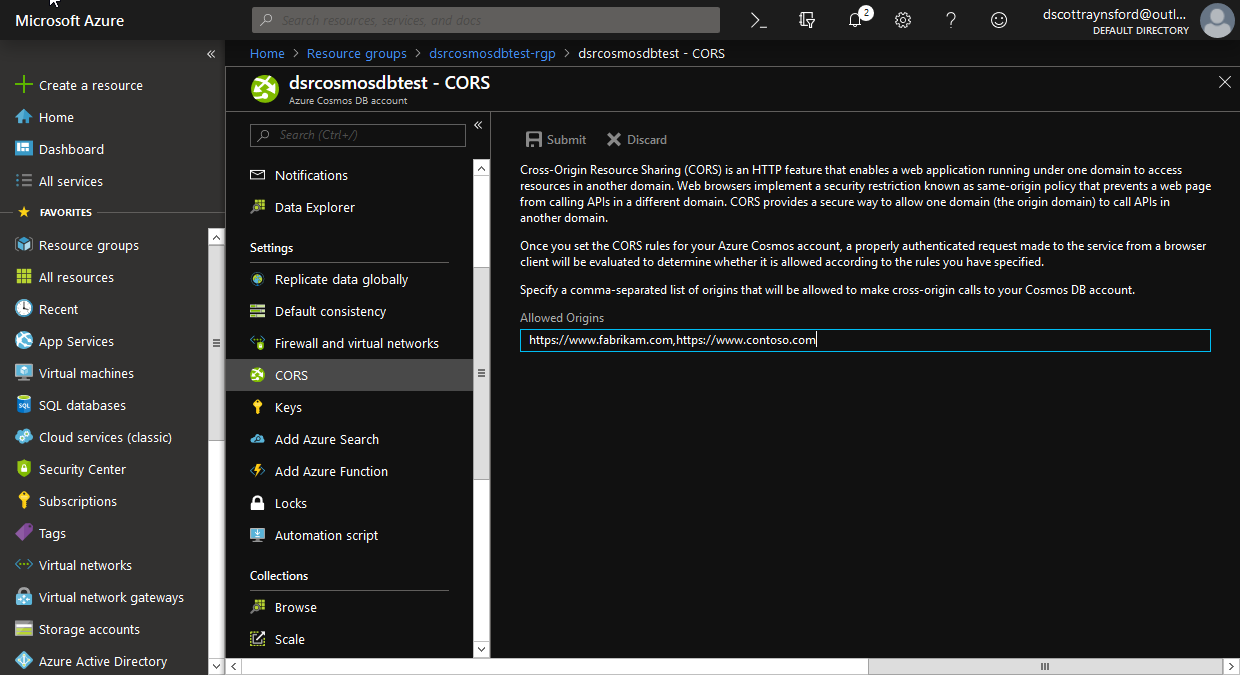
If you look in the Azure Portal, you will find the new Cosmos DB account with the CORS allowed origin values set as per your command:
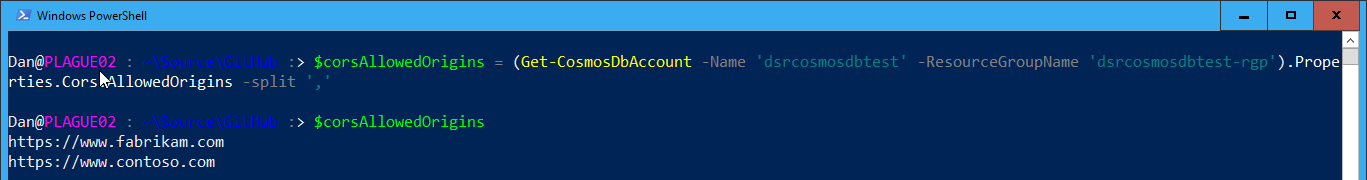
Getting the current CORS Allowed Origins value on an account is easy too. Just run the following PowerShell command:

This will return a string containing all the CORS Allowed Origins for the Cosmos DB account dsrcosmosdbtest.
You could easily split this string into an array variable by using:
To set the CORS Allowed Origins on an existing account use the Set-CosmosDbAccount function:
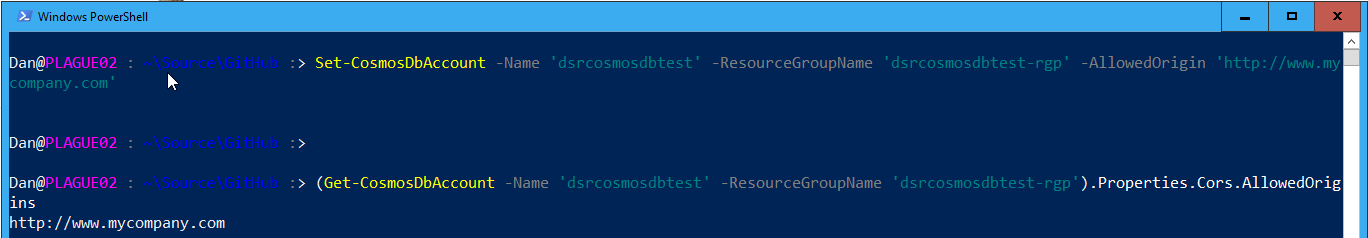
This will take a few minutes to update. So you can use the -AsJob parameter to run this as a Job.
You can remove the CORS Allowed Origins setting by setting using the Set-CosmosDbAccount function but passing in an empty string to the AllowedOrigin parameter:
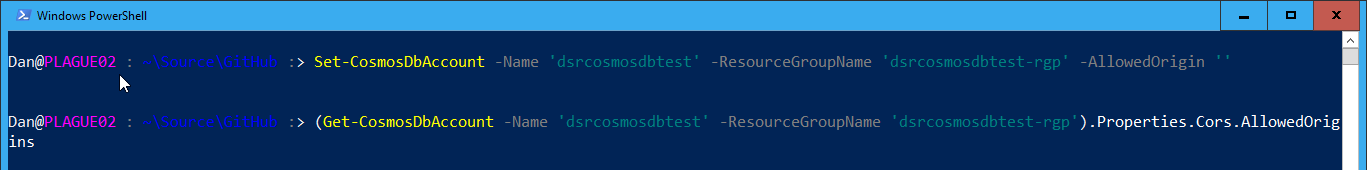
This will take a few minutes to update as well. As always, you can use the -AsJob parameter to run this as a Job.
Hopefully, you can see it is fairly simple to automate and work with the Cosmos DB CORS Allowed Origins setting using the PowerShell Cosmos DB module.
If you have any issues or queries or would like to contribute to the PowerShell Cosmos DB module, please head over to the GitHub repository.

