Managing Users & Permissions in Cosmos DB with PowerShell
If you’re just getting started with Cosmos DB, you might not have come across users and permissions in a Cosmos DB database. However, there are certain use cases where managing users and permissions are necessary. For example, if you’re wanting to be able to limit access to a particular resource (e.g. a collection, document, stored procedure) by user.
The most common usage scenario for users and permissions is if you’re implementing a Resource Token Broker type pattern, allowing client applications to directly access the Cosmos DB database.
Side note: The Cosmos DB implementation of users and permissions only provides authorization - it does not provide authentication. It would be up to your own implementation to manage the authentication. In most cases you’d use something like Azure Active Directory to provide an authentication layer.
But if you go hunting through the Azure Management Portal Cosmos DB data explorer (or Azure Storage Explorer) you won’t find any way to configure or even view users and permissions.
To manage users and permissions you need to use the Cosmos DB API directly or one of the SDKs.
But to make Cosmos DB users and permissions easier to manage from PowerShell, I created the Cosmos DB PowerShell module. This is an open source project hosted on GitHub. The Cosmos DB module allows you to manage much more than just users and permissions, but for this post I just wanted to start with these.
This module works on PowerShell 5.x and PowerShell Core 6.0.0. It probably works on PowerShell 3 and 4, but I don’t have any more machines running this version to test on.
The Cosmos DB module does not have any dependencies, except if you call the New-Cosmos DbContext function with the ResourceGroup parameter specified as this will use the AzureRM PowerShell modules to read the Master Key for the connection directly from your Cosmos DB account. So I’d recommend installing the Azure PowerShell modules or if you’re using PowerShell 6.0, install the AzureRM.NetCore modules.
The best way to install the Cosmos DB PowerShell module is from the PowerShell Gallery. To install it for only your user account execute this PowerShell command:
Install-Module -Name CosmosDB -Scope CurrentUser

Or to install it for all users on the machine (requires administrator permissions):
Install-Module -Name CosmosDB

As of Cosmos DB module v2.0.1, the connection parameter has been renamed to context and the New-CosmosDbConnection function has been renamed New-CosmosDbContext. This was to be more inline with naming adopted by the Azure PowerShell project. The old connection parameters and New-CosmosDbConnection function is still available as an alias, so older scripts won’t break. But these should be changed to use the new naming if possible as I plan to deprecate the connection version at some point in the future.
This post was updated to specify the new naming, but screenshots still show the Connection aliases.
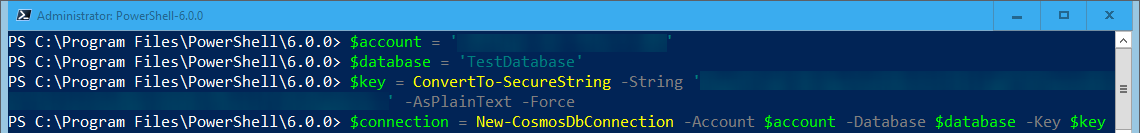
Before you get down to the process of working with Cosmos DB resources, you’ll need to create a context variable containing the information required to connect. This requires the following information:
- The Cosmos DB Account name
- The Cosmos DB Database name
- The Master Key for the account (you can have the Cosmos DB PowerShell module get this directly from your Azure account if you wish).
To create the connection variable we just use the New-CosmosDbContext:
If you do not wish to specify your master key, you can have the New-CosmosDbContext function pull your master key from the Azure Management Portal directly:
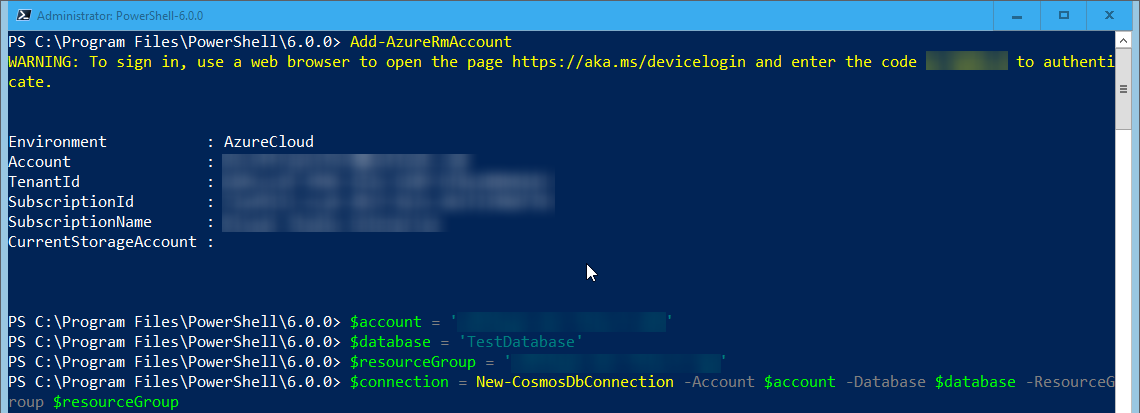
Note: This requires the AzureRM.Profile and AzureRM.Resoures module on Windows PowerShell 5.x or AzureRM.Profile.NetCore and AzureRM.Resources.NetCore on PoweShell Core 6.0.0.
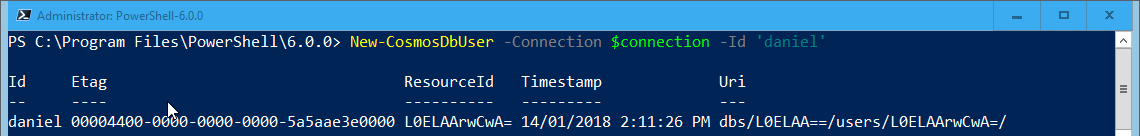
To add a user to the Cosmos DB Database use the New-CosmosDBUser function:
New-CosmosDbUser -Context $context -Id ‘daniel’
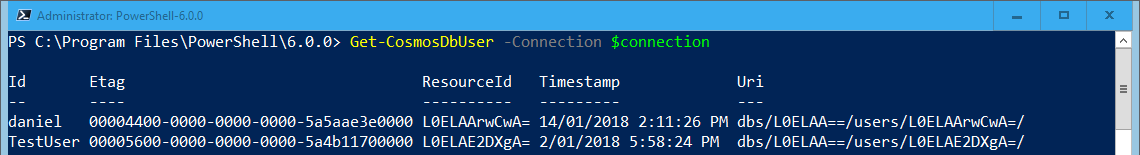
To get a list of users in the database:
Get-CosmosDbUser -Context $context
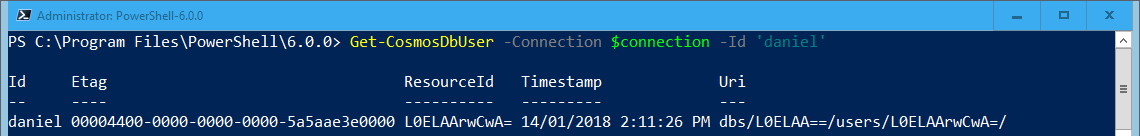
To get a specific user:
Get-CosmosDbUser -Context $context -Id ‘daniel’
To remove a user (this will also remove all permissions assigned to the user):
Remove-CosmosDbUser -Context $context -Id ‘daniel’

Permissions in Cosmos DB are granted to a user for a specific resource. For example, you could grant a user access to just a single document, an entire collection or to a stored procedure.
To grant a permission you need to provide four pieces of information:
- The Id of the user to grant the permission to.
- An Id for the permission to create. This is just string to uniquely identify the permission.
- The permission mode to the permission: All or Read.
- The Id of the resource to grant access to. This can be generated from one of the Get-CosmosDb*ResourcePath functions in the CosmosDB PowerShell module.
In the following example, we’ll grant the user daniel all access to the TestCollection:
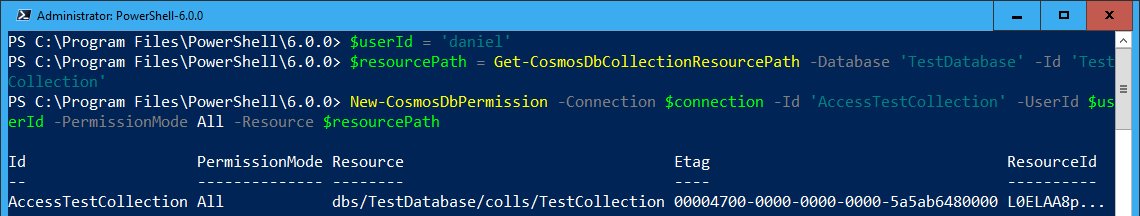
Once a permission has been granted, you can use the Get-CosmosDbPermission function to retrieve the permission and with it the Resource Token that can be used to access the resource for a limited amount of time (between 10 minutes and 5 hours).
Note: as you have the Master Key already, using the Resource Token isn’t required.
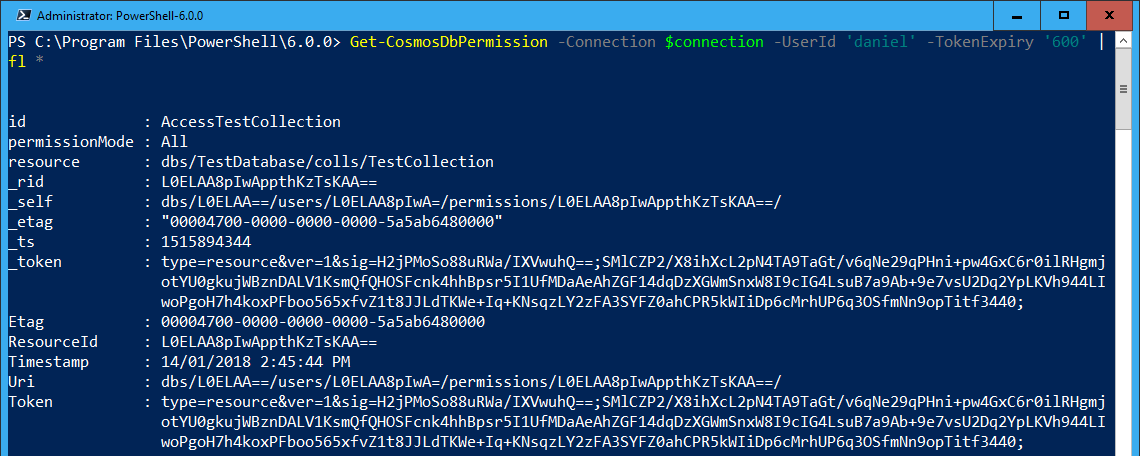
For example, to retrieve all permissions for the user with Id daniel and a resource token expiration of 600 seconds:
Get-CosmosDbPermission -Context $context -UserId ‘daniel’ -TokenExpiry ‘600’ | fl *
You can as expected delete a permission by using the Remove-CosmosDbPermission function:
Remove-CosmosDbPermission -Context $context -UserId ‘daniel’ -Id ‘AccessTestCollection’

So this is pretty much all there is to managing users and permissions using the Cosmos DB PowerShell module. This module can also be used to manage the following Cosmos DB resources:
- Attachments
- Collections
- Databases
- Documents
- Offers
- Stored procedures
- Triggers
- User Defined Functions
You can find additional documentation and examples of how to manage these resources over in the Cosmos DB PowerShell module readme file on GitHub.
Hopefully this will help you in any Cosmos DB automation tasks you might need to implement.
