Multiple VHD/VHDx Optimization using PowerShell Workflows
Like most tech people I have lots of Hyper-V VM’s scattered across various computers at home. Some of these VM’s are running on Server OS hosts (Server 2012 R2) and some running on client OS hosts (Windows 8.1) on my desktop or laptop. These VMs also get varying amount of use - lab and dev machines getting used most of the time while “experimentation” machines getting booted only rarely.
I also like to run my heavily used VMs on fast SSD drives to keep them “snappy”. But like most people I have only a limited amount of SSD space. I’m also quite an obsessive neat freak. These two things combined means I like to keep the VHD/VHDx files used by my VMs as small as possible.
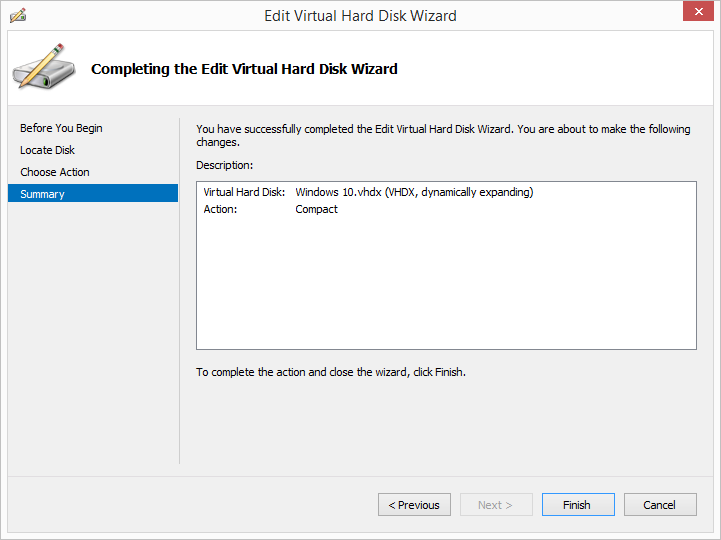
Keeping VHD/VHDx files trim is can easily be performed inside the Hyper-V management tool by clicking the Edit Disk… button and using the Edit Virtual Hard Disk Wizard to Compact the desired VHD/VHDx file:
This of course is all a bit manual and can be really time-consuming when performing this on lots of virtual hard disks. This sounds like it could be performed by a PowerShell command.
After about 5 minutes of investigation I came up with this simple PowerShell command:
Get-VM | Where { $_.State -eq ‘Off’ } | Get-VMHardDiskDrive | Optimize-VHD -Mode Full
It basically performs a full optimization on all VHD/VHDx files attached to all Virtual Machines that are in the Off state on the host the command is run on. This does the job quite well but has a few annoyances:
- The optimization is performed in series.
- Running guests won’t be optimized.
- The command only works on VMs on the host the command is run on.
Looking at the list of annoyances it seems a PowerShell workflow might be a good solution. So, after a few hours coding and testing (I can’t tell the number of times my VMs were rebooted and optimized over the day) I managed to complete a module containing a PS Workflow that was up to the task (documentation contained in the link):
Optimize Hyper-V VHDs using PowerShell Workflow
The module can be installed into a PowerShell modules folder (or imported from any location) and the workflow called like in the same way a normal cmdlet would be called:
Optimize-VHDsWorkflow -ComputerName HV-01,HV-02 -VMName NTB01,NTB02,NTB03 -Mode Quick
The above command would optimize all VHD/VHDx files attached to VMs called NTB01, NTB02 or NTB03 on hosts HV-01 and HV-02. It would perform this optimization in parallel meaning all VHDs would be optimized at the same time. Care obviously needs to be taken here, because optimizing too many VHDs running off the same data store could saturate the IO leading to performance of the data store being crippled.
When this workflow is run, any VMs that are running will not have their VHDs optimized. This is probably a good thing for production guests, but for my test lab guest, I want them to be shutdown automatically, have their VHDs optimized and have them automatically started back up. So I implemented a switch called AllowRestart:
Optimize-VHDsWorkflow -AllowRestart -Mode Full -Verbose
The AllowRestart switch will allow a guests that are in a running state to be shut down (not turned off or forced), an optimization performed and then started back up. If a guest is not in a running state it will just be optimized. If the guest can’t be shut down using a normal shut down (because the guest doesn’t have Hyper-V tools running or installed or isn’t running a compatible OS) then it won’t be optimized.
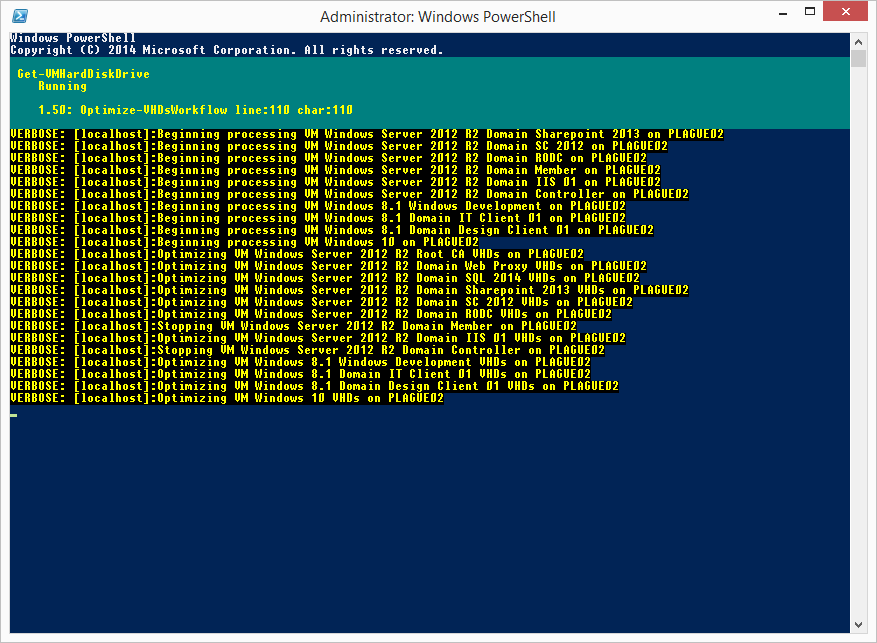
You can also use the Verbose switch to show more information about the workflow process:
There really isn’t much to the process and it could even be scheduled via Task Manager to be performed automatically. If anyone has any comments or feature requests, please let me know - I’m always enjoy a challenge!
\m/ \m/